Anatomy
- Breast
- Cardiovascular
- Digestive System
- Musculoskeletal
- Neurological System
- Reproductive/Endocrine Thoracic Cavity
- Urinary System
- Lymphatic System
Basic structures
- Integument - outer protective layer, skin
- Protection (UV, microoganisms, chemical, thermal)
- Sensations (pain, temperature, touch, pressure)
- Thermoregulation
- Metabolic (e.g. vitamin D synthesis)
- Fascia - band/sheet of connective tissue
- Stabilizes muscles and organs
- Compartmentalizes - determines spread of infection and cancer
- Bone - connective tissue, mineralized extracellular matrix with bone cells inside
- Structural framework
- Locomotion
- Calcium homeostasis
- Synthesis of blood cells
- Joints - unions between bones, fibrous outer layer lined by serous synovial membrane
- Movement
- Stabilized by ligaments attached to other bones and tendons attached to muscles
- Muscle - striated skeletal, striated cardiac, smooth muscle (walls of vessels and organs, viscera)
- Skeletal is voluntary, others are involuntary
- Locomotion
- Circulatory system - cardiovascular and lymphatic systems to transport fluids through the body
- Cardiovascular - oxygen and nutrients (in blood) to tissues, and CO2 and waste from tissues
- Exchanges in capillary beds
- Lymphatics - returns excess fluid, foreign microorganisms, large plasma and proteins, lipids, lymphocytes
- Node filter cells, particulates, produce antibodies, initiate immune response
- Right side to right lymphatic ducts
- Left side to thoracic duct
- Both sides then to venous system near right side of heart
- Cardiovascular - oxygen and nutrients (in blood) to tissues, and CO2 and waste from tissues
Breast
Cardiovascular
Thorax - clavicle to diaphragm
Mediastinum - central compartment of the thoracic cavity
Includes heart + vessels, esophagus, trachea, phrenic and cardiac nerves, thoracic duct, thymus, central lymph nodes.
Intercostal neurovascular bundle running in costal groove is VAN (vein, artery, nerve), superior to inferior.
The heart - sinus rhythm and imaging view examples
Heart and vessels
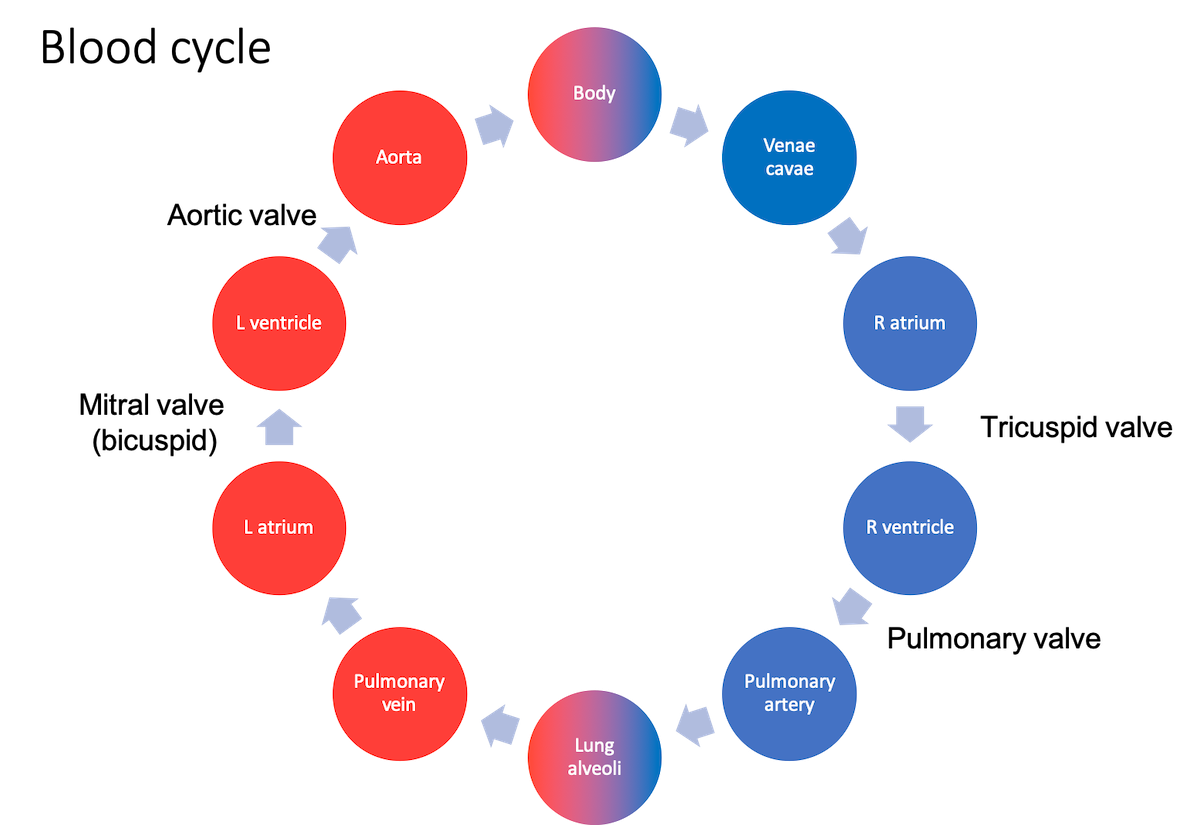
Right atrium - superior and inferior vena cava enter into it, deliver deoxygenated blood
Right ventricle - blood travels into it from right atrium through right cupid valve, flows out of pulmonary tricuspid valve through the pulmonary trunk to lungs
Left atrium - base of the heart, receives oxygenated blood from lungs
Left ventricle - receives blood from left atrium and pumps throughout body through the aorta. Thicker walls than right ventricle to generate higher pressures.
Superior vena cava - drains blood from structures above diaphragm (except heart and lungs) to right atrium.
Inferior vena cava - drains blood from structures below diaphragm, passing through a central tendon at the T8 vertebra.
Azygos vein - runs up the side of the thoracic vertebral column, draining blood from posterior walls of the thorax towards the superior vena cava. Connects also to inferior vena cava.
Systolic - end contraction pressure, ~ 120 mmHg
Diastolic - end filling pressure, ~ 50 mmHg
Pulmonary System
Pulmonary trunk - vessel that transports deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs. Within the pericardial sac. Bifurcates into left and right pulmonary arteries (underneath aortic arch).
Pleurae - Serous membranes surrounding lungs. Cavity between pleura is empty other than lubricating fluid (helps lungs expand with thoracic wall)
Lungs - light, spongy, elastic. Right lung has three lobes, left has two.
Trachea divides (the carina) into left and right bronchi , to secondary (lobar) bronchi, to tertiary (segmental) bronchi. Then bronchiole to alveoli for gas exchange
Segments are the functional units of the lung.
In lungs only, arteries carry deoxygenated blood (from heart) and veins carry oxygenated blood (to heart).
Alveoli - Air sacs, sites of gas exchange in lungs
Metastasis is enabled by veins that don't have valves - vertebral, pelvic and head & neck.
Circle of Willis - A circle of arteries at the base of the brain that supply blood to the brain. Around the pituitary.
Circulation path: Right atrium → Right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary vein → Lt atrium → Lt ventricle→ Aorta → body → vena cava
Diaphragm
Aids in breathing, separates thorax and abdomen. Openings allow passage of inferior vena cava, aorta, esophagus.
Digestive System
Liver - on right from 10th rib to 5th rib.
Detoxifies, synthesizes proteins, produces chemicals for digestion of proteins, lipids, carbs.
Gallbladder - at lower part of liver (9th rib). Aides in fat digestion. Releases stored bile, created in liver, into duodenum
Spleen - left ride, deep to 9-11th ribs
Pancreas - head in concavity of duodenum, body at L2 vertebra, curves up to hilum of spleen. (middle-ish)
Kidneys - left and right, posterior, upper poles near 11th and 12th ribs. Right slightly lower than left (liver presence)
Ureters - hilum of kidney, inferior to psoas muscle, to bladder (can be visualized by pyelogram)
Small intestine
- Duodenum - ~ 1 foot, receives from chyme from stomach (through pyloric sphincter), bile from liver, and enzymes from pancreas, which is surrounds. Digestion.
- Jejunum - ~ 3 feet, much digestion and absorption using villi. Proteins and carbs.
- Ilium - ~ 6 feet, even more digestion and absorption of nutrients, B12 and bile acids.
Celiac artery: supplies blood to foregut (stomach, liver, spleen, lower esophagus, upper pancreas and duodenum.
Musculoskeletal
Spine
Vertebra
- 7 cervical
- C1 is atlas (nod yes) connecting to C2 axis dens (odontoid process) for large range of motion of head (shake no)
- C3-C6 Larynx
- 12 thoracic
- Support ribs
- 5 lumbar
- Weight bearing
- Spinal cord ends at L1-L2 (cauda equina starts)
- Umbilicus at L3-L4
- 5 sacral (fused)
- Connects spine to hips (pelvis)
- 4 coccygeal
- Fused bones, attachment of ligaments and muscle of pelvic floor
Vertebra are composed of a body, a vertebral arch (cord goes through it), and processes for muscle attachments
Separated by disks proving cushion (annulus surrounding fluid sac)
Ulna is larger on top (includes the elbow) and smaller near write, goes to pinky
Radius is smaller on top and larger near wrist, goes to thumb
Pelvis - sacrum (middle of pelvis, holes for nerves); innominate bone including ilium (top of pelvic bone), ischium (lateral bottom of pelvic bone) and pubis (medial bottom bone); symphysis pubis (joint between sides of pelvis); obturator foramen (opening formed by pubis and ischium for VAN).
Foramen magnum - opening at base of skull (occipital bone) for medulla oblongata.
Cerebellum - bottom of skull, posterior. Motor control, coordination, balance, some cognitive functions (attention, fear, pleasure, language).
Axial skeleton: skull, spine, ribs
Appendicular skeleton: scapula, arms, legs, pelvis
Neurological System
Spinal cord starts after medulla oblongata (just below foramen magnum) and ends around L2. Cauda equina just below cord. Dural/thecal sac ends at S2 (sheath of dura mater around cord and cauda equina with cerebral spinal fluid).
31 spinal nerves with dorsal and ventral root
Dorsal receives from skin (afferent) and ventral sends to muscle (efferent)
Dermatones - regions of skin innervated by specific nerves.
Brachial plexus - network (plexus) of nerves, emerges at spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1, going to chest, shoulder, arm and hand.
Medulla oblongata - Long part of brain stem, controls autonomic functions (breathing, digestion, heart/vessel function, sneezing).
Pons - Part of brain stem, connects cerebral cortex to medulla oblongata. Communication and coordination between hemispheres.
Limbic system - "emotional brain", between cerebrum and brain stem.
Hippocampus (memory), hypothalamus (heart-rate, respiration, emotional response), amygdala (agression), thalamus (sensory relay)
Corpus callosum - connects cerebral hemispheres.
Choroid plexus - network of blood vessels each ventricle, produces cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
Cranial nerves
- Olfactory Nerve: sensory; smell
- Optic Nerve: sensory; vision
- Oculomotor Nerve: motor; movement of upper eyelid and eyeball
- Trochlear Nerve: motor; movement of eyeball
- Trigeminal Nerve: mixed; conveys impulses for touch, pain, temp sensations, chewing
- Abducens Nerve: motor; movement of eyeball
- Facial Nerve: mixed; touch, pain, taste, temp sensations, facial expression, secretion of saliva and tears
- Vestibulocochlear Nerve: sensory; equilibrium, hearing
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve: mixed; taste, somatic sensations, blood regulation, swallowing and speech, secretion of saliva
- Vagus Nerve: mixed; taste, somatic sensations, blood regulation, breathing, sensations in visceral organs in throat and abdomen, swallowing, coughing, voice production, muscle GI tract
Spinal cord segments
- 8 cervical pairs (1 more than vertebra)
- 12 thoracic pairs
- 5 lumbar pairs
- 5 sacral pair
- 1 coccygeal pair (4 fused vertebra)
Ventricles (produce and store CSF): Four total - 1 right and 2 left lateral, 3 superior to hypothalamus and between halves of thalamus, 4 between brainstem and cerebellum.
Reproductive/Endocrine Thoracic Cavity
Endocrine glands:
Hypothalamus - Base of brain, just above pituitary and optic chiasma
Releases hormones, regulates temperature, maintain physiological cycles, regulate emotional responses.
- Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
- Oxytocin
- Vassopressin - regulate water retentino
Stimulates pituitary gland with:
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) - helps with function of many organs like heart, GI, muscles
- Somatostatin - stop releasing certain hormones (growth, thyroid stimulants)
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) - induces production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
Pituitary gland - In pituitary fossa below optic chiasma
Pineal gland - aka epiphysis, produces melatonin (seratonin-derived hormone), modulate sleep patterns
Thyroid gland -
Parathyroid glands -
Islet cells of the pancreas -
Adrenal glands -
Testes -
Ovaries -
Uterus is spooning the bladder
Urinary System
Kidneys - left and right, posterior, upper poles near 11th and 12th ribs. Right slightly lower than left (liver presence)
Ureters - hilum of kidney, inferior to psoas muscle, to bladder (can be visualized by pyelogram)
Lymphatic System
Thoracic duct receives lymph from lower half of body and left side of upper body. Drains into venous system near left internal jugular and left subclavian veins (right side drains to right jugular and subclavian).
Thymus - Organ responsible for maturation of T-cells. Large bi-lobed organ within superior and anterior of mediastinum.
Axillary lymph nodes - important to breast cancer metastasis
- lateral group medial to axillary vein
- Pectoral group inferior to border of pectoralis muscle
- Subscapular group posterior to axillary fold
- Central group deep to pec minor
- Apical group at apex of axilla
Spleen - Filters old blood cells, removes stores and produces white blood cells (lymphoctyes) to produce antibodies and remove microbes from blood.