Other topics and more details related to NM and PET are included in the links below
Posts tagged with '-'
Found 8 posts
Radiopharmaceuticals/radiotracers are radioactive compounds used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic compounds use photons emitted from a radioactive isotope attached to the compound to image where the compound goes in the body.
Effective half-life:
1/Teff = 1/Tbio + 1/Tphys
λeff = λbio + λphys
Imaging
Note: doses and imaging protocols are possible choices, not definitive.
PET and Gamma/SPECT imaging
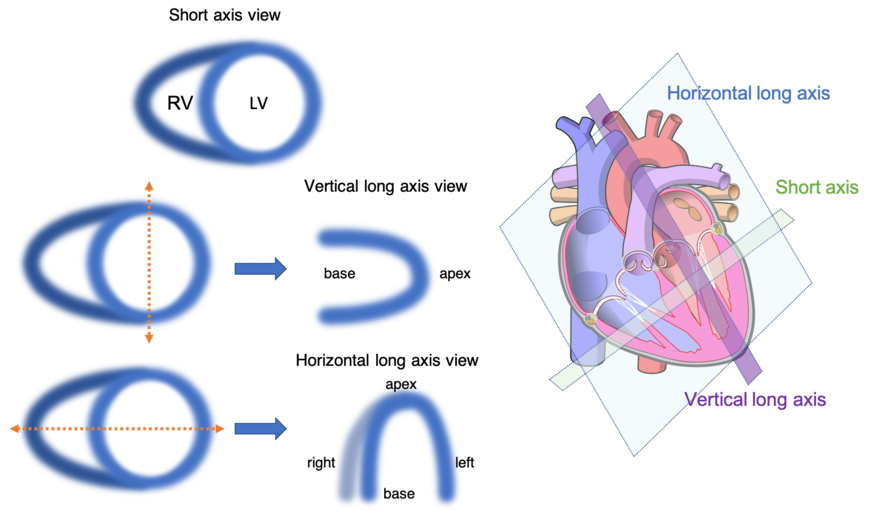
Cardiac
- Tc-99m Sestamibi, "Mibi" (Cardiolite)
- Target: Myocardial perfusion
- Uptake: Lipophilic cation diffuses from blood to myocardium. Taken up by cells with high mitochondria concentration (e.g. myocardium). 60% first pass, minimal clearance. See also parathyroid
- Indications: Coronary artery disease (CAD), chest pain, pre-surgical
- Dose: ~ 10 mCi rest, 30 mCi stress, IV (~9 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: 45-60 minutes uptake to allow for clearance of tracer from the lungs and liver. Typically image at rest and stress to look for reversible ischemia (exercise stress) or impaired cardiac flow reserve (pharmacologic stress).
- Notes: Most common myocardial perfusion agent,
- Th-201 Chloride
- Target: Myocardial perfusion
- Uptake: Active transport, potassium analog, though cellular sodium-potassium pump
- Indications: Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Dose: 2-4 mCi (~15 mSv)
- Imaging protocol:
- Notes: lower energy photons means lower resolution images vs. Tc-99m tracers
- 99mTc-Tetrofosmin (Myoview)
- Target: Myocardium
- Uptake: Myocytes, metabolism dependent (within 5 min). Not cation channel transport. (diffusion?)
- Indications: CAD, heart disease (ventricular function)
- Dose: 5-33 mCi (~10 mCi rest, ~30 mCi stress) (~8 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: 15 min, ~ 4hour between rest and stress.
- Notes: Rest/stress to look for ischemia and infarction; perfusion changes from pharm stress; left ventricular function (ejection fraction).
- 99mTc-PYP (Pyrophosphate)
- Target: transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR).
- Uptake: Possibly due to high calcium levels (bone seeking)
- Indications: Transthyretin amyloidosis (high uptake), distinguish from light-chain amyloidosis (low uptake)
- Dose: 10-15 mCi (~ 3 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: 1 hour uptake, SPECT and planar. 3 hr optional
- Notes: Originally a bone seeking agent.
- 99mTc-labeled red blood cells (RBC), "MUGA"
- Target: Blood pool
- Uptake: Autologous radiolabeled blood cells in circulation via injection
- Indications: CAD, acute myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, drug therapy (chemo) assessment
- Dose: 15-30 mCi (~ 6.5 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: ECG gated (16 frames/cycle), rest and stress
- Notes: MUGA (A multi-gated cardiac blood pool scan). Evaluate cardiotoxic chemotherapy. Qualitative and quantitative, functional parameters possible.
Bone
- 99mTc-MDP (Tc-99m-methyl diphosphonate) and 99mTc-HDP (Tc-99m Oxidronate (TechneScan))
- Target: Bone
- Uptake: Adsorbs onto the crystalline hydroxyapatite mineral of bone
- Indications: Osteomyelitis, fractures, cancers (osteoid osteoma, bone mets, sarcomas), scoliosis, ossifications, calcinosis, pulmonary calcification, sickle cell disease
- Dose: 20-30 mCi (~ 5 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: whole-body planar, limited area planar, multi phase scintigraphy - blood flow (dyn), blood pool/soft tissue (10 min), skeletal (2-4 hours), SPECT
- Notes: MDP of the most common NM scans, (HDP 2nd most common bone scan). Uptake in bone-forming pathology or growth regions of immature bone (osteoblasts). Uptake is dependent on blood flow to the bone and extraction efficiency.
- 18F-NaF
- Target: Bone
- Uptake: Exchange diffusion. Fluoride absorption directly onto the surface of the bone matrix, exchanges with hydroxide ion, hydroxyapatite is converted to fluorapatite. Distribution corresponds to osseous blood flow and osteoblastic activity.
- Indications: Similar to MDP and HDP
- Dose: 5-10 mCi (~7.5 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: 30-45 min uptake, longer for extremities. 2-5 min/bed
- Notes: Not common, more expensive than scintigraphy.
Renal
- 99mTc-MAG-3 (mercapto acetyl tri glycine)
- Target: Kidney
- Uptake: Tubular secretion, excretion by both glomerular filtration and tubular excretion;
- Indications: Kidney disease, transplants, evaluating the functioning of kidneys.
- Dose: 3-10 mCi (~1.3 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: Dynamic planar: 60 sec flow, then every 5 min for 25 min
- Notes: ROI over kidneys to measure activity (uptake and clearance) over time. Correlates with effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). Better than DTPA for peds and patients with poor renal function. Rapid transit, not good for SPECT.
- 99mTc-DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentacetate)
- Target: Kidney
- Uptake: filtered by the glomerulus, measure glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Indications: Kidney disease, transplant, evaluating the functioning of kidneys.
- Dose: 1-30 mCi (5 mCi ~ 0.9 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: Dynamic planar: 60 sec flow, then every 5 min for 25 min
- Notes: Rapid transit, not good for SPECT. ROI over kidneys to measure activity (uptake and clearance) over time.
- 99mTc-DMSA (2,3 dimercaptosuccinic acid)
- Target: Kidney
- Uptake: Binds to plasma proteins. ~50% fixed to kidney cortex
- Indications: Evaluate renal structure and morphology (peds), scarring, renal tract infection
- Dose: 5-10 mCi (5 mCi ~ 1.6 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: Dynamic planar: 60 sec flow, then every 5 min for 25 min
- Notes: Rapid transit, not good for SPECT. ROI over kidneys to measure activity (uptake and clearance) over time
GI bleeding
- 99mTc-labeled red blood cells (RBC)
- Target: GI tract
- Uptake: Introduced into anatomical compartment
- Indications: GI bleeding
- Dose: 25 mCi
- Imaging protocol: 1 sec frames for 60 sec, 1 min for 60-90 min, delayed 6-8-24 hrs. hot spots conforming to anatomy
- Notes: Delivery failure or leakage indicates compromised compartment
Hepatobiliary
- 99mTc-Disofenin (Hepatolite), 99mTc-Mebrofenin (Choletec)
- Target: Biliary
- Uptake:
- Indications: Biliary pain, acute cholecystitis, bile leakage , neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, transplants, gallbladder ejection fraction (GBEF), assessment of the liver before partial hepatectomy
- Dose: 3-5 mCi (2.5 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: 2-4 hr fast. Planar and SPECT. Dynamic 1 minute frames for 60 minutes. Delayed imaging 3-4 hr for some indications.
- Notes: measure the function of liver, gallbladder and bile ducts and detect any anatomical changes in the hepatobliary system. Mebrofenin has higher hepatic extraction and preferred for hyperbilirubinemia.
- 99mTc-HIDA (Cholescintigraphy)
- Target: Hepatobillary
- Uptake:
- Indications: Hepatobillary trauma, acute or chronic cholecystitis, biliary atresia in neonates, bile leak, biliary obstruction
- Dose:
- Imaging protocol: 4 hr fast. 60 minutes dynamic imaging.
- Notes: Slow movement - blockage, poor liver function, no tracer in gallbladder - acute inflammation, low GBEF - chronic inflammation, tracer in other areas - leakage.
Lung
For ventilation/perfusion studies (V/Q), ventilation is often performed first because of lower dose/uptake, although negative results in perfusions can make ventilation study unnecessary or provide guidance.
- 99mTc-MAA (Macroaggregated albumin)
- Target: Lung (pulmonary perfusion)
- Uptake: Capillary blockage - mechanical trapping in capillary bed because of 'large' size (5-100 um). 90% trapped in lung capillaries first pass (0.00003% blocked)
- Indications: Pulmonary embolism, cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders
- Dose: 2-5 mCi (~ 1.2 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: V/Q, immediate imaging with injection over 3-5 respiratory cycles. Upright or supine. Planar anterior, posterior, obliques, laterals.
- Notes: Records the distribution of pulmonary arterial blood flow. Brain uptake indicates R-L shunt.
- 99mTc-DTPA aerosol (diethylenetriaminepentacetate)
- Target: Lung
- Uptake:
- Indications:
- Dose: 25-35 mCi nebulized, 0.5-1 mCi to lungs
- Imaging protocol: Aerorsol (30 mCi) for V/Q (ventilation/perfusion) lung ventilation, image immediately for 5 minutes
- Notes: Records bronchopulmonary distribution of an inhaled radioactive aerosol within the lungs
- 133Xe gas
- Target: Lung ventilation
- Uptake: Inhaled, <15% of gas absorbed, short (30 sec) bio halflife
- Indications: Pulmonary embolism, cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders.
- Dose: 5-20 mCi (~0.3 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: Planar views during administration and after. Upright if possible, posterior and posterior obliques during wash in and washout
- Notes: Often performed with perfusion scan. Retention - COPD, mucus plugging, asthma. Also cerebral blood flow. Records pulmonary distribution of a radioactive gas during breathing
Brain
- 99mTc-Exametazime, HMPAO (Ceretec)
- Target: Cerebral perfusion
- Uptake: Lipophilic, converted to hydrophilic in cells.
- Indications: Altered perfusion after stroke, brain death, dementia, neurological defects
- Dose: 15-30 mCi (6.9 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: SPECT, 90 min post injection
- Notes: Can be complemented with pharmaceutical agents that enhance regional cerebral blood flow (acetazolamide)
- 99mTc-Bicisate (Neurolite, ECD)
- Target: Brain
- Uptake: Diffusion, according to concentration gradients
- Indications: Stroke
- Dose:
- Imaging protocol:
- Notes: Shows cerebral blood flow
- I-123 ioflupane (DaTScan)
- Target: Dopamine system (striatum)
- Uptake: Cocaine analog, high affinity for presynaptic dopamine transporters (DAT)
- Indications: Parkinsons
- Dose: 3-5 mCi (4.4 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: SPECT 3-6 hours post injection, 30-45 min total
- Notes: Demonstrates the location and concentration (e.g., degeneration) of dopamine transporters (DaTs) in the synapses of striatal dopaminergic neurons.
- Tracer
- Target:
- Uptake:
- Indications:
- Dose:
- Imaging protocol:
- Notes:
Cancer
- 18F-FDG
- Target: Cancer, inflammation
- Uptake: Glucose analog, trapped after phosphorylation
- Indications: Cancer, suspected metastasis, infection of unknown origin
- Dose: 10-15 mCi (8.4 mCi)
- Imaging protocol: PET imaging after 60 minutes uptake, 3-5 min/bed depending on BMI
- Notes: Most common cancer and PET imaging agent (90% of studies). Often use SUV as quantitative metric and to track changes over time/treatments
- 68Ga-DOTATATE/TOC
- Target: Neuroendocrine tumors, meningiomas
- Uptake: Binds to SSTR2 receptors
- Indications: Suspected/known neuroendocrine tumor
- Dose: 3-5 mCi (~3.2 mSv)
- Imaging protocol: PET imaging after 60 minute uptake
- Notes:
- Tracer
- Target:
- Uptake:
- Indications:
- Dose:
- Imaging protocol:
- Notes:
Therapy
I-131 - beta emitter, Thyroid. Also has imageable but high energy photons
Lu-177 DOTATATE - beta emitter for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT). Treats cancers expressing somatostatin receptors (SSTR2), especially neuroendocrine tumors (NET). Theranostic pair with 68Ga-DOTATATE, but can also image photons from Lu-177.
Lu-177 PSMA - beta emitter that targets PSMA for prostate cancer therapy. Theranostic pair with 68Ga-PSMA, but can also image photons from Lu-177.
Y-90 microspheres - beta emitter for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Glass or resin beans act through capillary blockage - mechanical trapping. Placed into vessel feeding tumor. Can image (poorly) with PET (low rate of pair production) or SPECT (bremsstrahlung from high energy electron emission).
To be continued
Tracers and compartment modeling is a critical tool for more advanced imaging applications.
Kinetic modeling uses time varying radiotracer distribution to extract additional information from an imaging session.
Useful to assess receptor binding, diffusion, active transport, metabolism, washout, excretion, etc.
Requires dynamic imaging - frames at specific times and durations during and after the introduction of a tracer.
Model applied to kinetics can extract physiologic quantities, e.g., perfusion in mL/min/g.
Ideal tracer: identical/relatable behavior to natural substance, does not alter physiological process (tracer <1% of endogenous compound). High specific activity → quality imaging and blood samples without altering physiology. Change in mass of isotope should not affect biochemistry ("isotope effect").
If labeled with a different radionuclide than naturally occurs, it should behave the same or in a predictably different manor, e.g. FDG not going through full cycle that glucose does (actually an advantage).
Dosimetry for injected/ingested/inhaled/absorbed radioactivity/radiopharmaceuticals.
Factors affecting internal dosimetry
- Route of exposure: inhalation, ingestion, IV injection, absorbtion
- Where did radioactivity go (e.g. thyroid, or excreted through bladder, etc)
- How long did it stay there (i.e. physical and biological half lives)
- What type of radiation at what energies?
- What type of patient (sex, age, etc.)
- Basic atomic and nuclear physics
- Interactions of photon and particle radiation with matter
- Radioactivity
- Sources of radioactive material
- Radioactive material uses and safety
- Radiation generating equipment: photons, electrons and heavy particles
- Dosimetry concepts and units
- Spatial distribution/transmission of radiation (photons, protons and electrons)
- Important dependencies